Table Of Content

For just as the greenhouse gas emissions from a century ago are inducing the climate change we see now, the emissions we release today will impact us long into the future. Electricity and heat productionThe IPCC's Fifth Assessment Report states that the burning of coal, oil, and gas to produce electricity and heat accounts for one-quarter of worldwide human-driven emissions, making it the largest single source. In the United States, according to EPA data, it’s the second-largest (behind transportation), responsible for about 28 percent of U.S. emissions in 2021, with carbon dioxide as the primary gas released, along with small amounts of methane and nitrous oxide. Of all the human-driven emissions of carbon dioxide, approximately half were generated in the last 30 years alone. The greenhouse effect is the natural warming of the earth that results when gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun that would otherwise escape into space. The world technically has only one-fifth of its "carbon budget"—the total is 2.8 trillion metric tons—remaining in order to avoid warming the Earth more than 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Climate Change Quiz
Due to the cutting of trees, there is a considerable increase in the greenhouse gases which increases the earth’s temperature. The greenhouse effect, combined with increasing levels of greenhouse gases and the resulting global warming, is expected to have profound implications, according to the near-universal consensus of scientists. Since 1750, nearly 1.5 trillion tons of carbon dioxide have been released into the atmosphere by human activities. Cumulatively, no country has emitted more carbon dioxide than the United States—approximately 25 percent of the global total—with the European Union and United Kingdom (EU-28) just behind it.
Greener tourism: Greater collaboration needed to tackle rising emissions
What is the greenhouse effect? Causes and consequences - Telefónica
What is the greenhouse effect? Causes and consequences.
Posted: Thu, 22 Jun 2023 07:59:33 GMT [source]
Today, concentrations of human-caused greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are higher than ever and the planet is heating up. Between preindustrial times and now, says the IPCC, the earth’s average temperature has increased almost 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1.1 degree Celsius), with two-thirds of that warming occurring in the last handful of decades alone. Earth’s greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere and warm the planet. The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor. In addition to these natural compounds, synthetic fluorinated gases also function as greenhouse gases. Different greenhouse gases have different chemical properties and are removed from the atmosphere, over time, by various processes.
Radiative balance
In other words, without Earth's atmosphere and the greenhouse effect it provides, we'd be up a creek. But it turns out that an overactive greenhouse effect can result a similarly devastating outcome. With too many heat-absorbing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, too much radiation gets trapped, causing the Earth to warm beyond its ideal temperature. It’s clear that decision makers, companies, leaders, and activists across the country and around the world staunchly believe we must all act on climate change.
Because the greenhouse effect is a natural process, it affects other bodies in the solar system, too. And, in some cases, that provides a warning about how things can go awry. A perfect example of this is Venus, which is roughly the same size as Earth and not that much closer to the sun.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
Another effect involves changes in precipitation, such as rain and snow. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change states that the global sea level rose about 1.8 millimeters (0.07 inches) per year from 1961 to 1993, and about 3.1 millimeters (0.12 inches) per year since 1993. As you might expect from the name, the greenhouse effect works … like a greenhouse! Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers. Although he said Scotland would still achieve its goal of net-zero carbon emissions by 2045, the decision sparked tensions with coalition partners. The Green Party initially backed the change, but party leaders said they would poll the broader membership and reverse course if necessary.
We calculated the UK's greenhouse gas emissions from people breathing out – here's what we found - The Conversation Indonesia
We calculated the UK's greenhouse gas emissions from people breathing out – here's what we found.
Posted: Wed, 13 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The greenhouse effect
In Earth's natural state, CO2 levels are kept in balance mostly by the activity of plant life. But as humans started burning more and more CO2-releasing fossil fuels, levels have shifted out of balance. Some of that released radiation makes it into space, and the rest of it ends up getting reflected back down to Earth when it hits certain things in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane gas and water vapor — the car windows. Currently, some scientists are investigating how to re-engineer the atmosphere to reverse global warming.
Atmosphere
Typically, a planet will be close to radiative equilibrium, with the rates of incoming and outgoing energy being well-balanced. Under such conditions, the planet's equilibrium temperature is determined by the mean solar irradiance and the planetary albedo (how much sunlight is reflected back to space instead of being absorbed). The power of outgoing longwave radiation emitted by a planet corresponds to the effective temperature of the planet. The effective temperature is the temperature that a planet radiating with a uniform temperature (a blackbody) would need to have in order to radiate the same amount of energy. Without the heating caused by the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average surface temperature would be only about −18 °C (0 °F). On Venus the very high concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes an extreme greenhouse effect resulting in surface temperatures as high as 450 °C (840 °F).
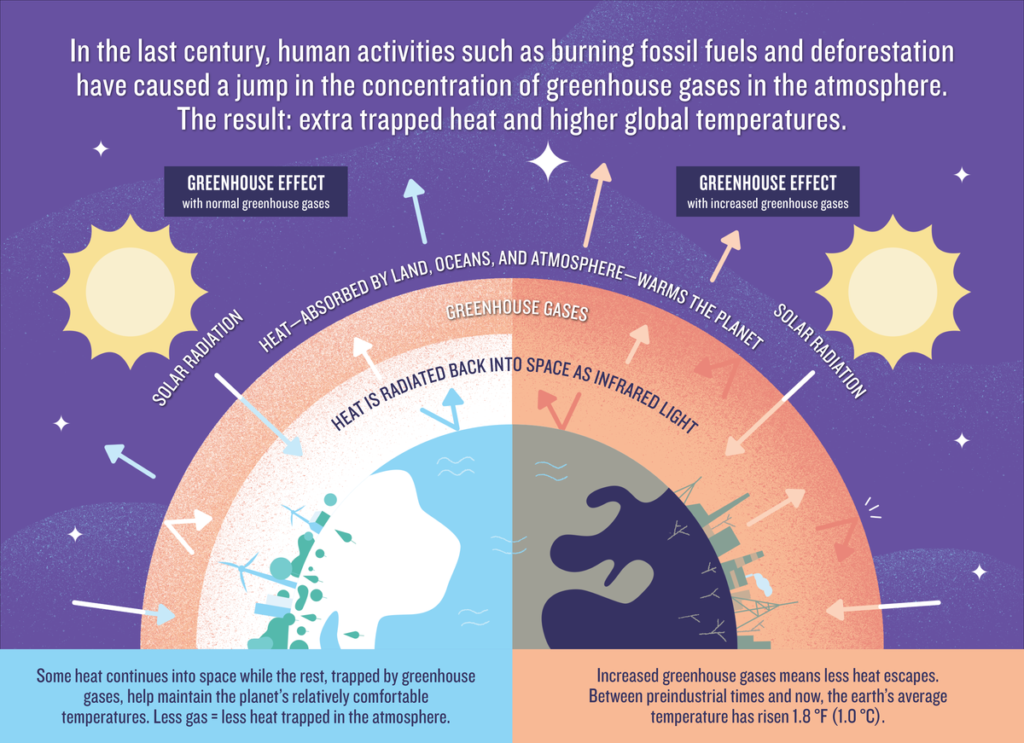
Too much of these greenhouse gases can cause Earth's atmosphere to trap more and more heat. The warmed Earth emits radiation upwards, just as a hot stove or bar heater radiates energy. In the absence of any atmosphere, the upward radiation from the Earth would balance the incoming energy absorbed from the Sun, with a mean surface temperature of around -18°C. The greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space.
Nearly a century later, American climate scientist James E. Hansen testified to Congress that “The greenhouse effect has been detected and is changing our climate now." But as the sun aged and grew brighter, excess water vapor would have entered Venus' atmosphere. While some people still doubt the reality of human-induced climate change, the evidence for it is overwhelming. Since the 1850s, the average global surface-air temperature has risen by around 1.4 F (0.8 C), and ocean temperatures are now at the highest levels ever recorded. Other greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, are emitted by human activity, at an unnatural and unsustainable level, but the molecules do occur naturally in Earth's atmosphere.
This has led to an increase in the release of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Agriculture and land useAbout another quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions stem from agriculture and other land uses, like deforestation, says the IPCC. In the United States, agricultural activities—primarily the raising of livestock and crops for food—accounted for 10 percent of greenhouse gas emissions in 2021. Of those, the vast majority were methane (which is produced as manure decomposes and as beef and dairy cows belch and pass gas) and nitrous oxide (often released with the use of nitrogen-heavy fertilizers). Radiative forcing (RF) is another way to measure greenhouse gases (and other climate drivers, such as the sun’s brightness and large volcanic eruptions). Also known as climate forcing, RF indicates the difference between how much of the sun’s energy gets absorbed by the earth and how much is released into space as a result of any one climate driver.
Finally, many different industries rely on carbon-rich fuels or other processes that give off CO2. All of these sectors can make changes to emit less CO2, but the same solutions won’t work for all of them. Carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas that drives global climate change, continues to rise every month. Fourier, however, neither used the term greenhouse effect nor credited atmospheric gases with keeping Earth warm. Swedish physicist and physical chemist Svante Arrhenius is credited with the origins of the term in 1896, with the publication of the first plausible climate model that explained how gases in Earth’s atmosphere trap heat.
In the 1970s, an abnormally long warm spell caused these Antarctic birds' population to drop by 50 percent. Some scientists worry that continued global warming will push the creatures to extinction by changing their habitat and food supply. Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of Earth's atmosphere. If carbon dioxide were removed, the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse, and Earth's surface temperature would drop significantly, by approximately 33°C (59°F).

No comments:
Post a Comment