Table Of Content
All of these human activities add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. The rise in Earth’s average temperature contributed to by human activity is known as global warming. The delicate balance of life on our planet hinges on a complex array of factors. From erupting volcanoes and wildfires, to deforestation and fossil fuels, the carbon cycle is affected by nature and human activities. For example, the voracious burning of fossil fuels for energy is artificially amping up the carbon dioxide greenhouse effect. This results in rising temperatures that are altering the planet’s climate system, causing catastrophic climate change.
Human Activity Is the Cause of Increased Greenhouse Gas Concentrations
Insight: World's war on greenhouse gas emissions has a military blind spot - Reuters
Insight: World's war on greenhouse gas emissions has a military blind spot.
Posted: Mon, 10 Jul 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Energy from the Sun that makes its way to Earth can have trouble finding its way back out to space. The greenhouse effect causes some of this energy to be waylaid in the atmosphere, absorbed and released by greenhouse gases. Gases which can absorb and emit longwave radiation are said to be infrared active[61] and act as greenhouse gases. Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse. Global warming describes the current rise in the average temperature of Earth’s air and oceans.
Atmosphere
Water vapour is the biggest overall contributor to the greenhouse effect. However, almost all the water vapour in the atmosphere comes from natural processes. The last time Earth's atmosphere had similar carbon dioxide concentrations was during the Pliocene epoch, between 3 million and 5 million years ago, according to the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in San Diego. That's at least 2.8 million years before modern humans roamed the planet. Fossils show that forests grew in the Canadian Arctic during the Pliocene, and savannas and woodlands spread over what's now the Sahara desert.
Water Crisis
The depletion of the ozone layer results in the entry of the harmful UV rays to the earth’s surface that might lead to skin cancer and can also change the climate drastically. Basically, Earth is not able to expel enough heat to keep itself cool, resulting in what's become known as "global warming." It's the greenhouse effect gone wild. The process gets its name from the greenhouses that stay nice and warm for growing plants. This is basically the same process that keeps Earth nice and warm for sustaining life. One example of the greenhouse effect that most of us experience in everyday life is the warming of a car's interior when the vehicle is left out in the sun.
Everyday Environmental Tips
The Conservatives and the opposition Labour Party had proposed separate no-confidence motions in Yousaf and his government amid efforts to weaken the SNP going into the general election. The SNP has been the dominant party in Scottish politics for almost two decades and currently holds 43 of Scotland's 59 seats in the U.K. Labour is likely to be the biggest beneficiary of the problems in the SNP because both parties share left-leaning policies. The greenhouse effect occurs in the atmosphere, and is an essential part of How the Earth System Works.
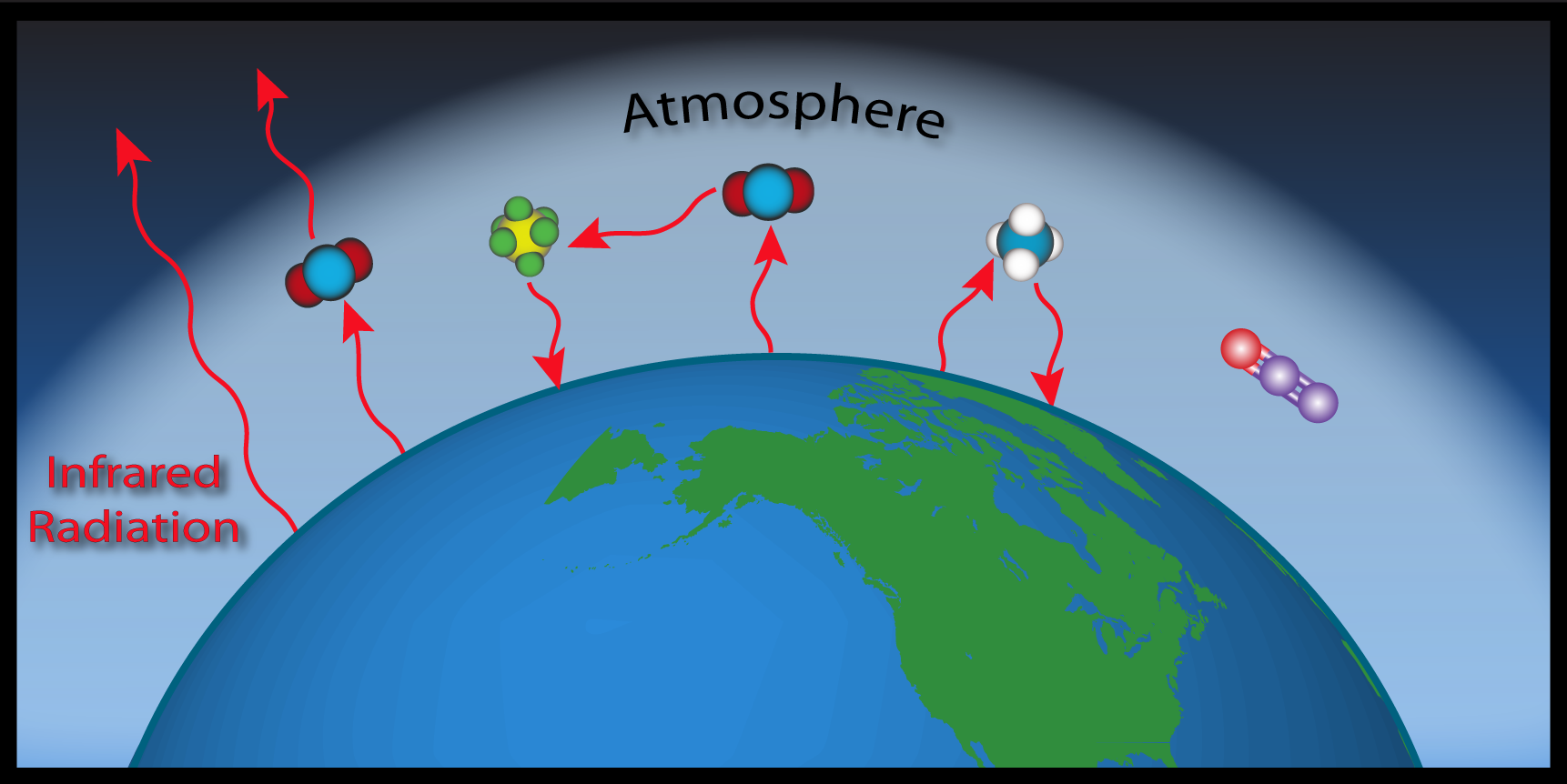
However, due to the increased levels of greenhouse gases, the temperature of the earth has increased considerably. If there were not any greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, all that heat would pass directly back into space. With greenhouse gases present, however, most of the long-wave radiation coming from Earth’s surface is absorbed and then re-radiated in all directions many times before passing back into space.
Other sourcesThis category includes emissions from energy-related activities other than fossil fuel combustion, such as the extraction, refining, processing, and transportation of oil, gas, and coal. Globally, according to the IPCC, this sector accounts for 9.6 percent of emissions. While fluorinated gases are far less prevalent than other GHGs and do not deplete the ozone layer like CFCs, they are still very powerful. Over a 20-year period, the global warming potential of some fluorinated gases is up to 16,300 times greater than that of CO2. Find out how global warming affects climate, and explore the different ways climate change is occurring.
Some greenhouse gases come from natural sources, for example, evaporation adds water vapor to the atmosphere. Animals and plants release carbon dioxide when they respire, or breathe. There is evidence that suggests methane is released in low-oxygen environments, such as swamps or landfills. Volcanoes—both on land and under the ocean—release greenhouse gases, so periods of high volcanic activity tend to be warmer. Today, concentrations of human-caused greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are higher than ever and the planet is heating up.
Greenhouse Effect 101
Heat that is re-radiated downward, toward the Earth, is absorbed by the surface and re-radiated again. However, absorbed sunlight increases the temperature of Earth’s surface, and the warmed surface re-radiates as long-wave radiation (also known as infrared radiation). The problem is mostly the increased concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). In simple terms, “tipping points” in climate change are synonymous to a seesaw. Just as a little weight can tip a seesaw and make it difficult to return to its original position, in the climate system, tipping points represent critical levels where small changes can lead to big and often irreversible shifts in weather patterns. Once these points are crossed, they can cause a chain reaction, with more emissions entering the atmosphere.
HFCs are used as a replacement for ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), usually in air conditioners and refrigerators, but some are being phased out because of their high GWP. Replacing these HFCs and properly disposing of them is considered to be one of the most important climate actions the world can take. From 2010 to 2021, policies were put in place to lower annual emissions by 11 gigatons by 2030 compared to what would have otherwise happened. Individuals can also join the UN’s #ActNow campaign for ideas to take climate-positive actions. During COP26, the European Union and the United States launched the Global Methane Pledge, which will see over 100 countries aim to reduce 30 per cent of methane emissions in the fuel, agriculture and waste sectors by 2030. The amount of CO2 in the atmosphere far exceeds the naturally occurring range seen during the last 650,000 years.
Climate change-driven droughts and floods also pose huge risks to agriculture. Research suggests that for every degree Celsius that the planet heats up, crop yields will go down 3 to 7 percent. Food insecurity can lead to mass human migration and political instability in regions all over the world.
This process, called the greenhouse effect, keeps the planet warm enough for life to exist. Without an atmosphere, our world would be as cold as the lifeless moon, which has an average temperature of minus 243 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 153 degrees Celsius) on its far side. Because of the greenhouse effect, Earth maintains an overall average temperature of around 59 F (15 C). The Greenhouse Effect and Climate ChangeEven slight increases in average global temperatures can have huge effects. Disappearing PenguinsEmperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) made a showbiz splash in the 2005 film March of the Penguins.
It's this equilibrium of incoming and outgoing radiation that makes the Earth habitable, with an average temperature of about 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius), according to NASA. Without this atmospheric equilibrium, Earth would be as cold and lifeless as its moon, or as blazing hot as Venus. The moon, which has almost no atmosphere, is about minus 243 F (minus 153 C) on its dark side. Venus, on the other hand, has a very dense atmosphere that traps solar radiation; the average temperature on Venus is about 864 F (462 C). Understanding the greenhouse effect and the role of different gases is pivotal to mitigating the impacts of climate change.
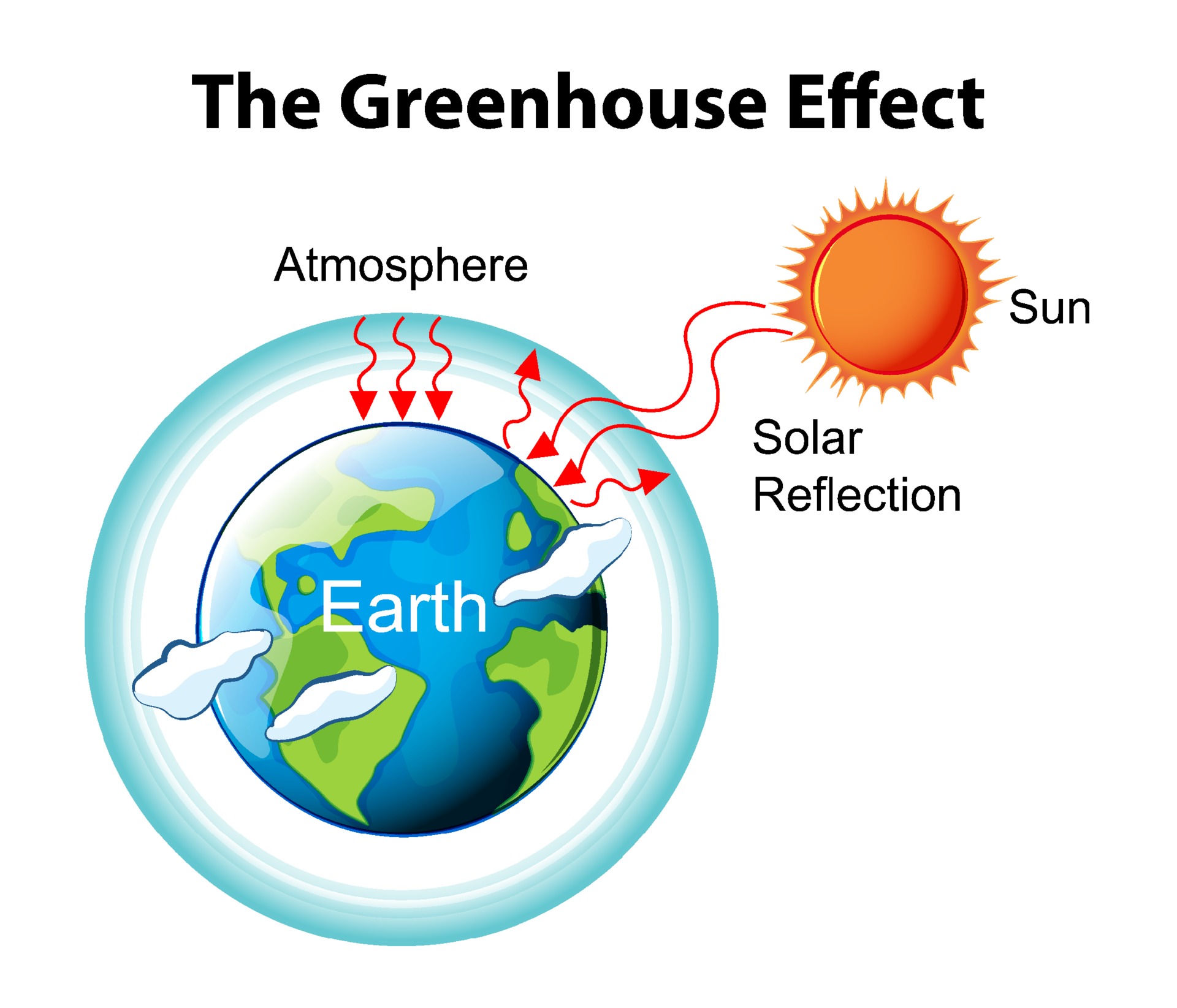
Much of the short wave solar radiation travels down through the Earth's atmosphere to the surface virtually unimpeded. Some of the solar radiation is reflected straight back into space by clouds and by the earth's surface. Much of the solar radiation is absorbed at the earth's surface, causing the surface and the lower parts of the atmosphere to warm.
This is what makes the surface of the earth warmer, that makes the survival of living beings on earth possible. The warming of the atmosphere that occurs when heat (longwave infrared radiation) is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. When people add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, Earth’s temperature rises. The earth has always experienced warm and cool phases, with natural forces—from the sun’s intensity, volcanic eruptions, and natural changes in greenhouse gas concentrations—affecting how much energy from the sun our planet absorbs. As recently as a couple of centuries ago, the planet underwent a “Little Ice Age,” caused by a decrease in solar activity and an increase in volcanic activity. But today’s warming—particularly the increase in temperatures since the mid-20th century—is occurring at a pace that can’t be explained by natural causes alone.

No comments:
Post a Comment